Monday, 2 June 2025
The things I do for QA...
A few years ago, I was among those who found Wayland too painful to use every day. Over time, I gave Wayland a try now and then. It finally got usable enough for me to switch to as my default a couple of years ago.
Recently, during the soft freeze before the Plasma 6.4 Beta was released, I used mainly X11 on both my laptops - for science! And by science, I mean regression testing. I was curious what the experience was like compared to what I've become accustomed to with Wayland.
In short, Wayland supports multiple displays and color so much better. It was painful using X11 again.
My setup for daily work
I was using two laptops and two external monitors. Both were running Plasma built from git-master.
- Main: Dell XPS laptop, plugged into a dock. This is connected to 2 ultrawide monitors - one via Displayport, the other via HDMI.
- Secondary: Lenovo Flex laptop, usually just using its built-in screen. Sometimes I swap the right hand monitor over to it, for testing display shenanigans.
Initial impression - so limited
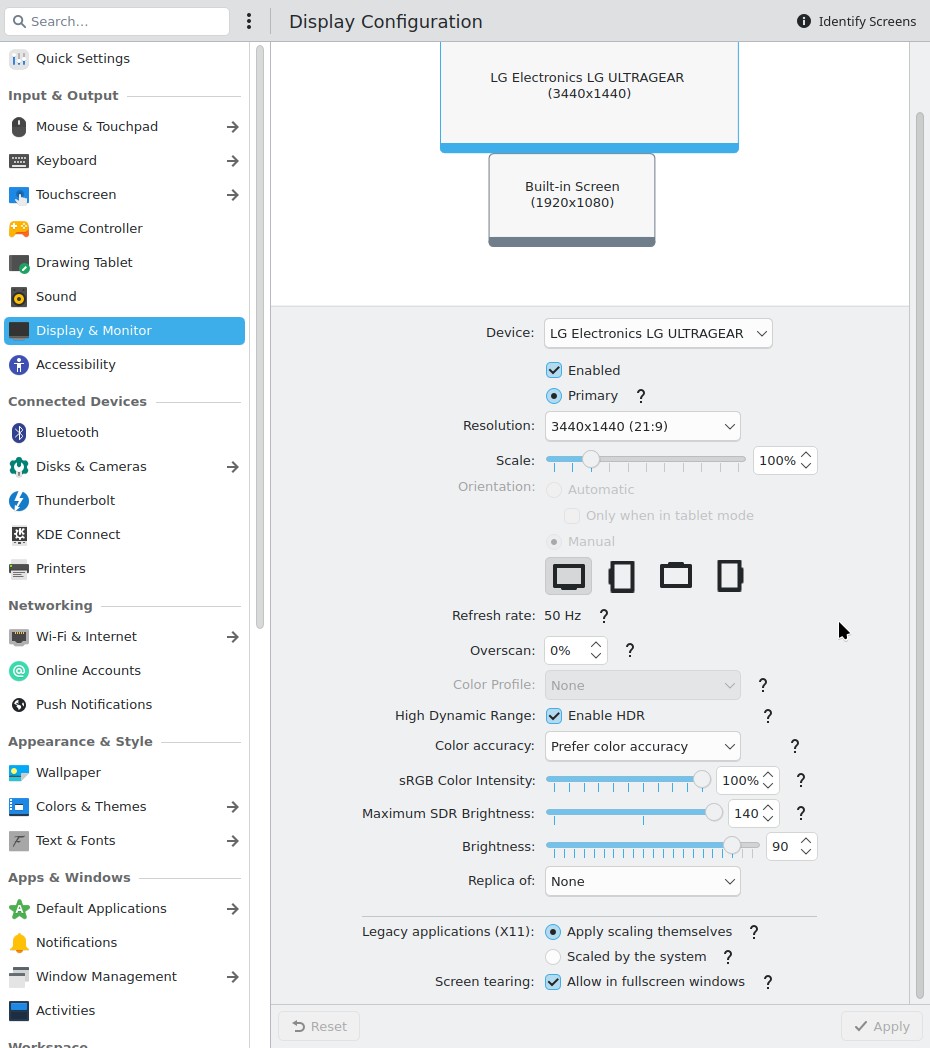
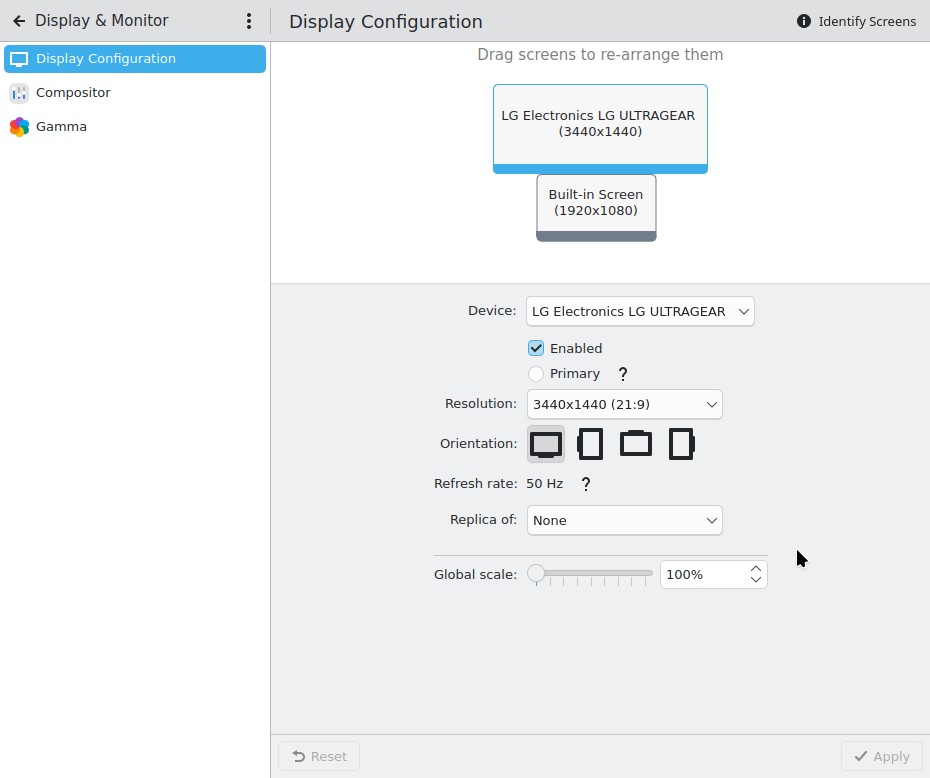
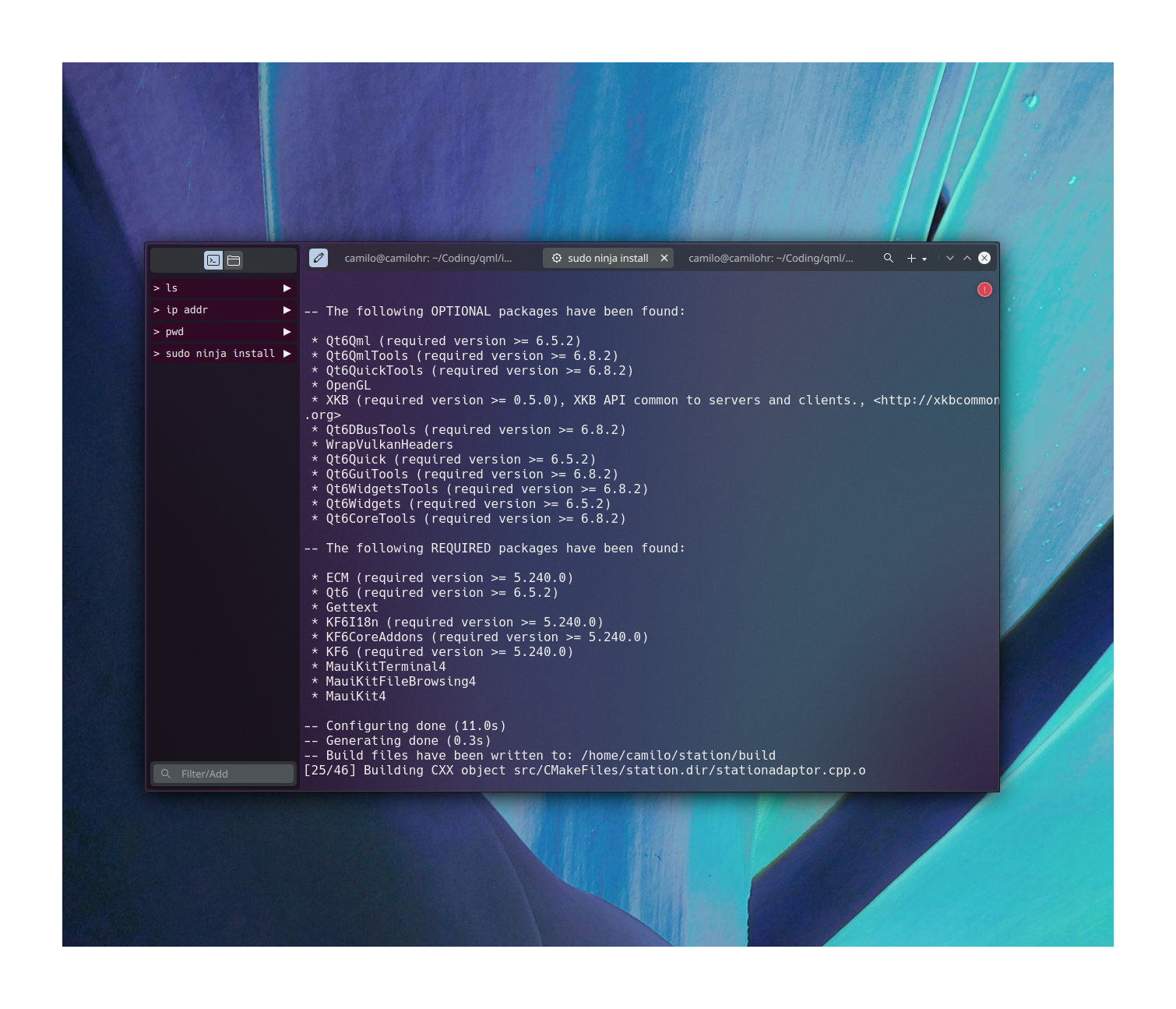
I fired up the XPS, did updates, and booted into an X11 session. Next, to Display Configuration to re-enable the right hand monitor (disabled the night before). Immediately, I was struck by how bare the settings window looks compared to Wayland. Here are screenshots of the settings for same HDR monitor on 6.3.5.
Wayland:
X11:
Second thoughts and hello, Dr Konqi
Time to enable the display. For reference, this takes moments in Wayland. It was just a wee bit longer and more fraught with X11.
After enabling the monitor and clicking Apply, all 3 screens went dark. After about 20s the laptop display came on. After about another minute, the right hand display finally got output before all 3 displays were dark again. I unplugged the laptop from the dock. It came up to the login screen. After logging in I saw the good Dr Konqi telling me there was a crash in plasmashell. We were off to a great start.
Like a good tester, I sent the crash report off. With some trepidation, I plugged the docking cable back in, as similar struggles from years past came back to haunt me. All three displays were black, although I could move the cursor around in them. It took a good couple of minutes for plasmashell to display everything, along with window decorations and panel contents. It was faster later, but wow, was this a noticeably worse experience than Wayland.
Other observations, or third thoughts
Wayland advantages
- Fractional scaling - the ability to have a screen at, say, 110% zoom. See that lovely screenshot, above.
When paired with how easy it is to change font face and style, this is great for accessibility. Being able to read the text on any display at whatever resolution can't be overstated. When I have to use Windows, where you can't adjust text separately from resolution, I have sadness. I also have eyestrain trying to read tiny text in dialogs. - Scaling per display - so my laptop's high resolution display can be at 150% and my external displays at 100% to make things readable on all of them. Another plus for accessibility.
- HDR and color profile (ICC) support. This is important for getting the mos out of my monitor with games and more. Also... preeeetty.
- Snappier overall performance (on my systems).
- The ability to send a window to multiple desktops, or just one. In X11, you can ....THNG
Wayland pain points
These are the things I ran into personally. There's also the list of Plasma/Wayland Known Significant Issues.
- The most annoying problem for me is with LibreOffice, since I use Calc almost daily. There's a bug (on their tracker) where, with multiple monitors with different scale factors, UI elements are too big.
- Lack of a robust, easy to use text expander with a GUI - that actually works out of the box. Autokey has been on my installs for many years, used for work and personal stuff. While it launches, and I have access to my phrases, there's no actual text expansion. There's an open issue for Wayland support (that pre-dates the Pandemic) but it hasn't gotten much traction. I've been keeping an eye out for years for a decent replacement, and have tried a few things but not found what I'm looking for, yet.
- Copy and paste to and from VMs I use VMs a lot for testing things on different Linux distros. My workaround for this is to have text files saved in a directory that's shared from host to guest.
- It took time and a few forks to get KVM software that was reliably developed and worked with Wayland.1 I had been using
barrieron X11. A few software forks and experiments later, I've settled ondeskflow.
X11 Advantages
- Remembering window positions across reboots.
- Working text expansion.
X11 pain points
- Drawing the screen is slower after logging in or restarting plasmashell, for example, with the same hardware and open applications.
- Floating panels and adaptive opacity are known to cause performance issues with X11 with an NVIDIA GPU.
- Lack of scaling per-monitor.
Text on my XPS's screen is too small to be readable if the external monitors are at a comfortable scale. I had to move any window I needed to read text on (most of them) to the external monitors. - The HDMI monitor was set to the wrong resolution and refresh rate if I connected it to the second laptop. I had to manually correct it.
- After enabling HDR on that monitor with the Flex in Wayland, and switching to an X11 session, the monitor enabled HDR but the colors were over-saturated.
- After working with a few windows, fonts in Firefox became badly hinted. This made characters look weirdly colored instead of white / black, and made reading things difficult.
Final thoughts
Once upon a time, Wayland was too painful for me to use as a daily driver. It didn't support some of my utilities and it wasn't stable enough with my multi-monitor setup.
These days, Wayland is so much more usable and stable with multiple displays that it makes using X11 painful by comparison. While there are still those few issues I mentioned, I feel Wayland's advantages outweigh them.
The KVM software journey... The first one I used was Synergy, which was amazing to me. Being able to use the same keyboard and mouse on both a Linux laptop and Windows desktop at the same time was magic. Unfortunately, Synergy took their UI in directions I didn't like. An open source fork named
barrieremerged, which aimed to restore the simplicity I was looking for, so I switched to it. This served me for a long time, but development stopped in 2021. With the advent of Wayland,barrierwas forked toinput-leapwhich implemented Wayland support. Sadly, development seems to have languished. There is yet another project,deskflow, which is also free and open source. It's sponsored by the Synergy folks. We end where we began. ↩︎






 #this-week-kde-apps:kde.org
#this-week-kde-apps:kde.org

 silver_hook
silver_hook


 I haven’t had time to blog, but today is my birthday and taking some time to myself!
I haven’t had time to blog, but today is my birthday and taking some time to myself!